Forging a carbon positive future...
|
The Carbon Story of Cellulose Insulation Understanding that carbon emission reductions within the built environment are a key strategy for mitigating climate change, CIMA sought to understand the challenges, benefits, and opportunities that exist within the insulation industry to accelerate carbon emission reductions. In 2023, in service to its mission, CIMA hired BfCA to conduct research to investigate these questions and to produce a report describing the findings for trade partners, material producers, government agencies, and policymakers. This report examines the potential for cellulose insulation to meet today’s requirements for low-carbon insulation products while also offering meaningful opportunities for carbon storage in line with CO2 removal targets. |
|
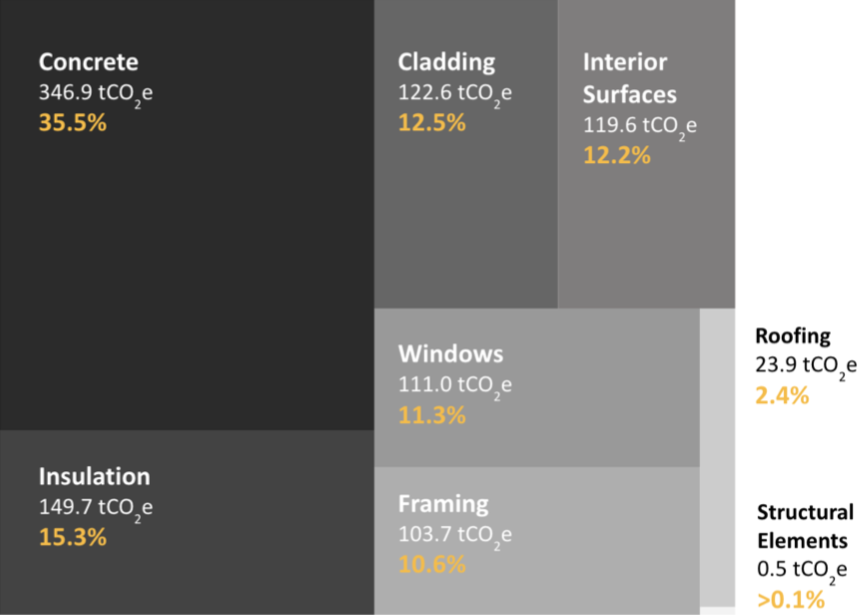
Vancouver Part 9 Material Emissions Benchmark Report The City of Vancouver is a world leader in addressing embodied carbon in the built environment, having set a target of reducing embodied carbon from new buildings by 40 percent by 2030. But in order to make reductions, there must first be a benchmark understanding of embodied carbon emissions in today’s new homes. This study examines 13 typical new homes using as-built plans to assess the carbon footprint attributable to the structure, enclosure and partitions of these homes. Using the BEAM estimator tool, each of the 13 homes was modeled, creating a valuable data set |
|
EMBARC Report
We partnered with Passive Buildings Canada to undertake the world's most comprehensive benchmark study of the carbon footprint of over 500 residential buildings, focusing on the Greater Toronto area. Funded by with The Atmospheric Fund. |
NRCan Study
This study explores the relationship between material emissions and operational emissions, examining 190 model homes across Canada. Ground breaking results on what's needed to achieve real net zero emission homes. |
Nelson Benchmark Study
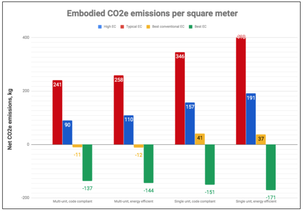
The cities of Nelson and Castlegar, BC wondered if there might be a material emissions penalty for homes achieving higher steps of energy efficiency. We found no direct correlation between material and operational emissions in these 34 homes. We also found that, on average, material emissions will outweigh operational emissions for 23 years! |
|
Nelson Material Carbon
Emissions Guide The City of Nelson used results from a beta version of our material emissions estimator to create a guide that quickly rates the carbon footprint of five high-impact material categories. This guide provides a highly visual and intuitive comparison of materials in categories with lots of competing products and big differences in emissions. |
BEAM Tool
More and more builders want to know: what is the carbon footprint of my building materials? And how can I reduce those impacts? We've built the BEAM estimator to help you, and we've made it easy to use and understand. Now you can transform your buildings. |
Build Beyond Zero book
Coming June, 2022 In Build Beyond Zero, carbon pioneers Bruce King and Chris Magwood re-envision buildings as one of our most practical and affordable climate solutions instead of leading drivers of climate change. They provide a snapshot of a beginning and map towards a carbon-smart built environment. |
|
Carbon-storing materials report
Builders for Climate Action's Director, Chris Magwood, was a co-author of this ground-breaking report from the Carbon Leadership Forum. The study found that a sizable reduction (~60%) in embodied carbon is possible in two to three years by bringing readily-available low-carbon materials into wider use. Furthermore, this work predicts that fostering a carbon-storing material supply system by investing in the development and manufacturing of nascent carbon-storing materials industries will make a carbon-positive future for individual projects possible in three to five years. |
|
Transformative Carbon-Storing Materials
Builders for Climate Action's Director, Chris Magwood, was a co-author of this ground-breaking report from the Carbon Leadership Forum. Findings from this study highlight six materials for use in building foundations, structures, and/or enclosure systems. These materials—earthen slabs, non-portland cement concrete slabs, algae-grown bricks/panels, mycelium structural tubes, purpose-grown fiber, and agricultural waste panels—warrant in-depth examination because they offer novel material technologies or novel material uses with high carbon-storing potential, and they are worthy of investment to accelerate their scaling, manufacturing, and marketable use in the building industry supply chain. |
|
White Paper #1
In 2019, our first white paper made a compelling case for immediate and profound action toward considering material emissions as an integral part of any zero carbon building strategy. The paper launched Builders for Climate Action and the BEAM tool. |
Opportunities for CO2 Capture and Storage in Building Materials
In 2018, Chris Magwood's produced a thesis paper that brought attention to the sizeable material emissions from low-rise residential buildings, and demonstrated the potential for carbon storing materials to eliminate all low-rise emissions. |